The Antimalware Service Executable is a crucial process within the Windows operating system, serving as the backbone for Windows Defender, the default antivirus software. Despite its importance, a significant number of PC users are unfamiliar with the nature and functionality of this process.
This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the Antimalware Service Executable, exploring its purpose, functionality, and potential impact on your computer’s performance. Through this discussion, you will understand the importance of this process in maintaining the safety and security of your PC.
What Is Antimalware Service Executable?
Microsoft Defender is a free antivirus software pre-installed on Windows 10 and 11. It replaced Microsoft Security Essentials, which was available for Windows 7. With Microsoft Defender, all Windows 10 and 11 users have an antivirus program installed and running, even if they haven’t chosen to install one.
If you have an outdated antivirus installed, Windows 10 or 11 will deactivate it and activate Microsoft Defender. The Antimalware Service Executable process is the background service for Microsoft Defender.
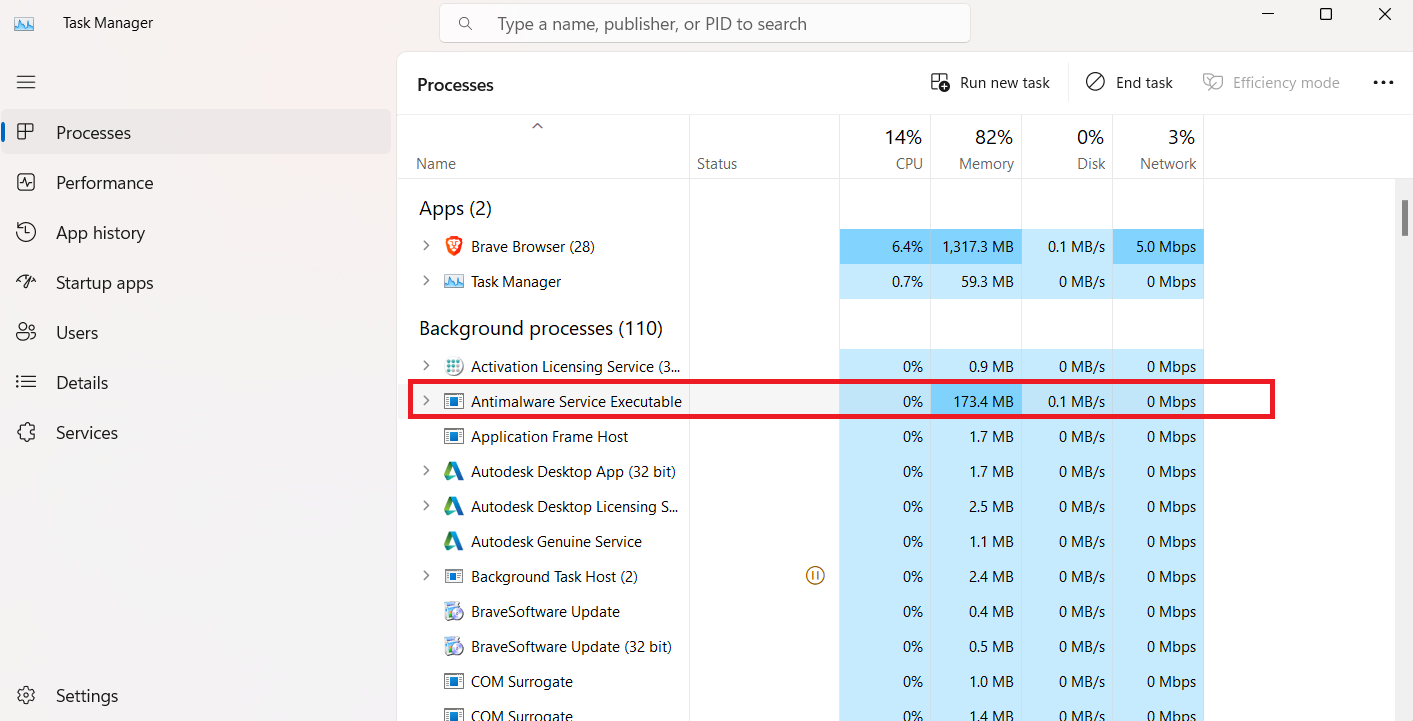
It continuously runs in the background, checking files for malware, conducting system scans for dangerous software, installing antivirus definition updates, and performing any other necessary tasks for the security application.
The Antimalware Service Executable process is also known as MsMpEng.exe, which you can find under the Details tab in Task Manager. You can manage Microsoft Defender by using the Windows Security application that comes with Windows 10 and 11. This app was previously called the “Windows Defender Security Center.”
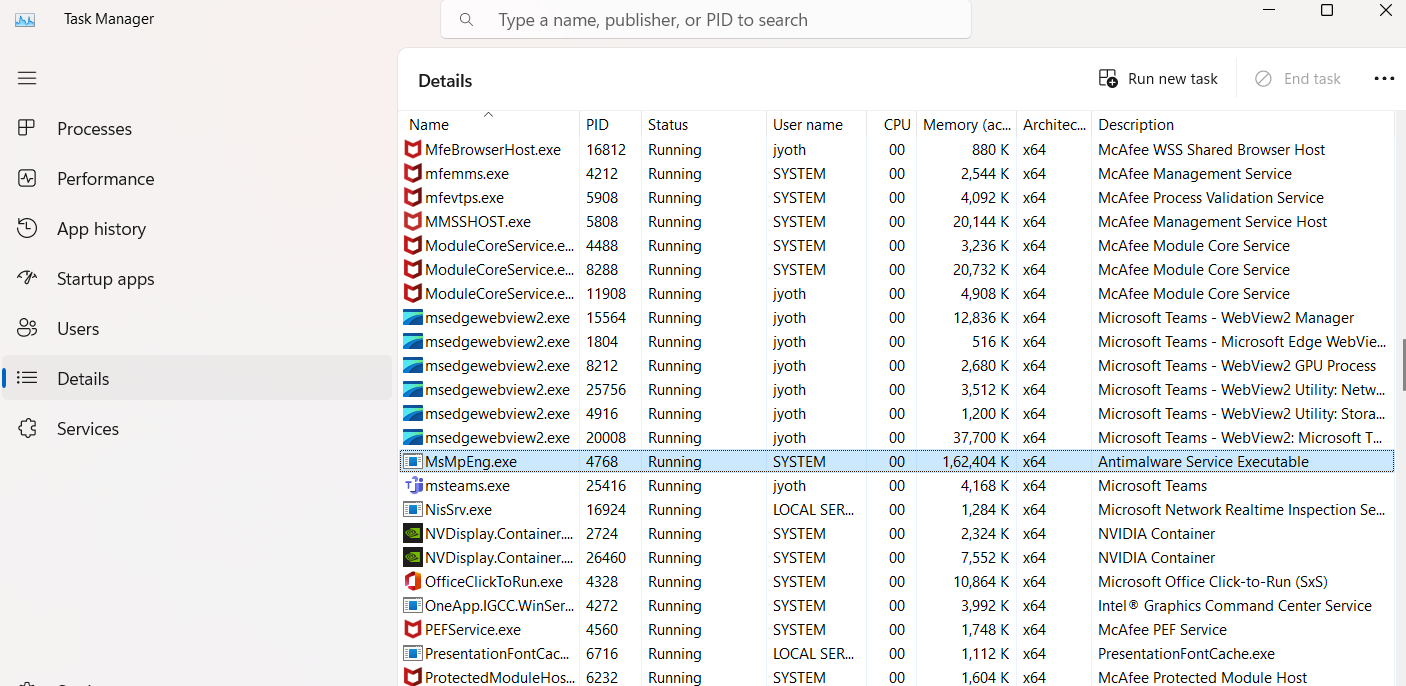
You can launch it using the “Windows Security” shortcut in the Start menu. Alternatively, you can right-click the shield icon on your taskbar’s notification area and select “View Security Dashboard.” You can also access it from Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security > Open Windows Security.
Why does Antimalware Service Executable use a High CPU?
MsMpEng.exe enables Windows Defender to monitor your PC for potential threats continuously. It provides real-time protection against viruses, malware, and cyberattacks. However, users have reported high CPU, memory, and disk usage caused by MsMpEng.exe because it constantly scans files and programs for malicious activity in the background.
This can be especially problematic for low-end computers, and full scans of all files can cause high CPU usage, leading to system lagging, hanging, and slow response times.
Possible causes of high CPU usage by MsMpEng include low hardware resources, conflicts with other Windows components or software, malware or virus infection, misconfigured or corrupt Windows system files, and outdated Windows Defender definitions.
To reduce CPU usage, one can disable the self-scanning function of Windows Defender, preventing it from scanning its folder through Windows Defender settings. However, this may reduce its effectiveness in detecting threats, so proceed cautiously and regularly check for updates and system scans.
How to fix ‘Antimalware Service Executable’ using a high CPU?
Do not remove or disable Windows Defender unless you have another IT security solution installed. It is crucial to have Windows Defender for protection against potential threats. Once Windows Defender has done its job and resolved any issues, follow these steps to prevent the Antimalware Service Executable issue from recurring:
1. Add it to the Windows Defender exclusion list
To fix the high CPU usage caused by Antimalware Service Executable, follow these steps:
- Press the “Windows logo + I” key and open the Settings window simultaneously.
- Click on Privacy & Security.
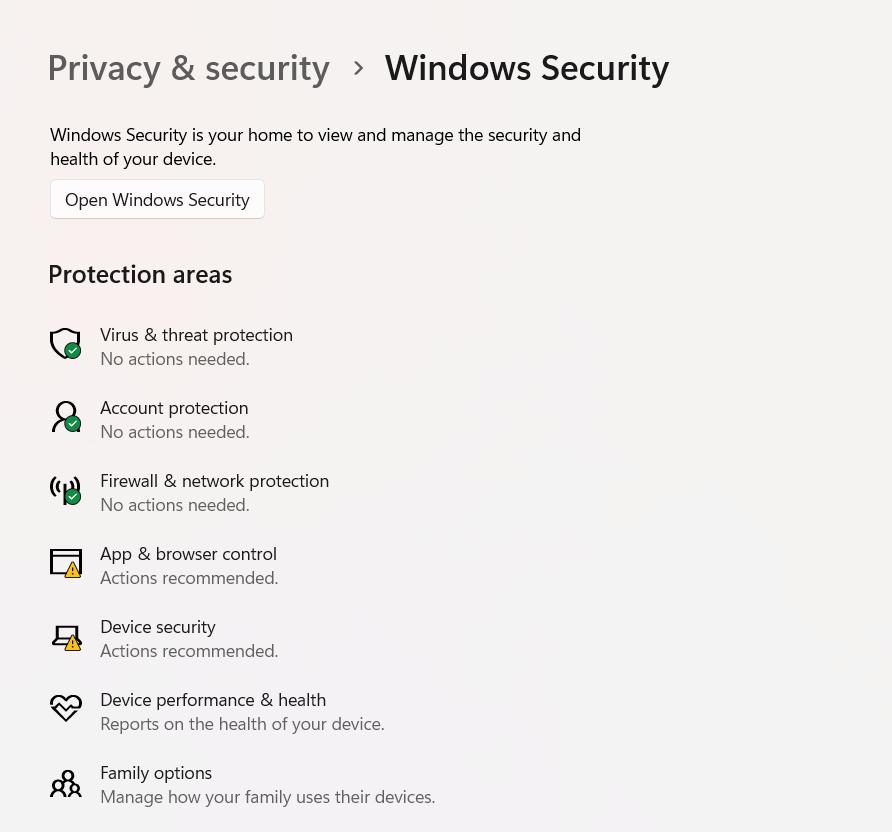
- Select Virus & threat protection under Windows Security and then click Manage settings.
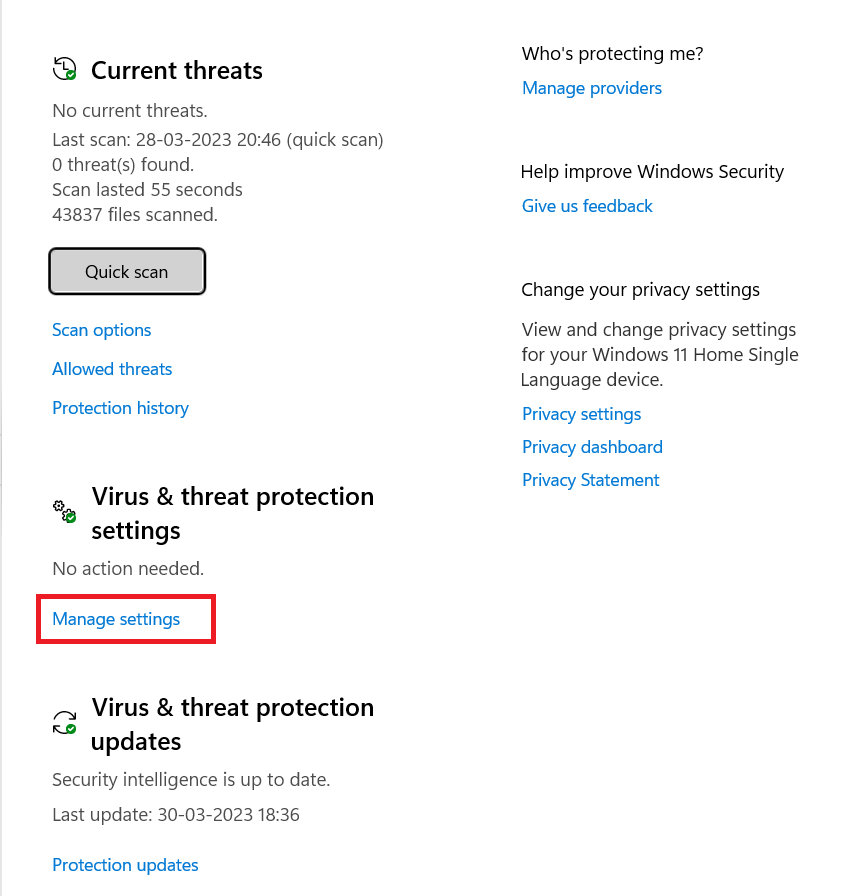
- Under Exclusions, choose Add or remove exclusions.
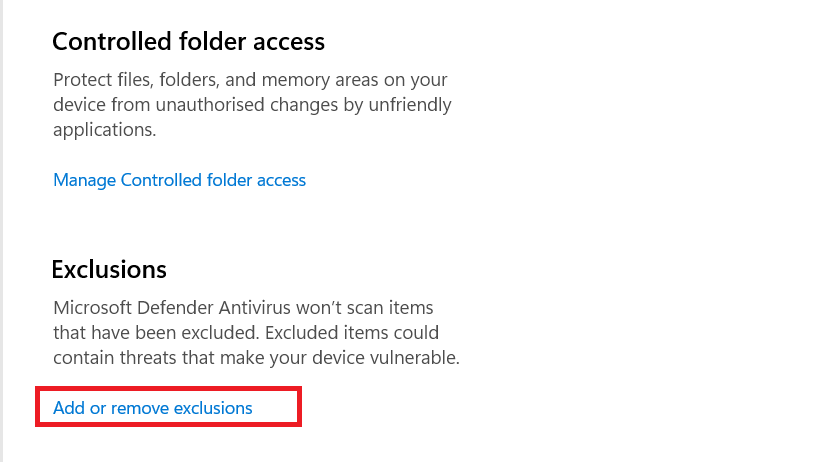
- Click Add an exclusion and select Process.
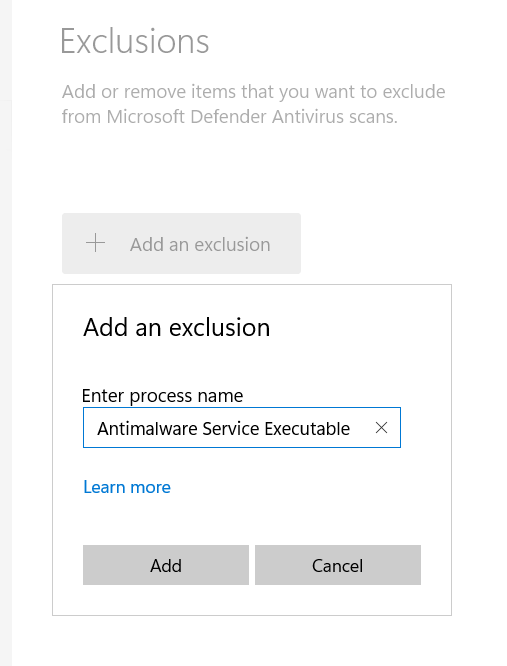
- Type in Antimalware Service Executable and click Add.
You have added Antimalware Service Executable to the Windows Defender exclusion list, which should fix the issue.
2. Reschedule Windows Defender’s
You can change the schedule to fix the error caused by Windows Defender’s real-time protection feature. Here’s how:
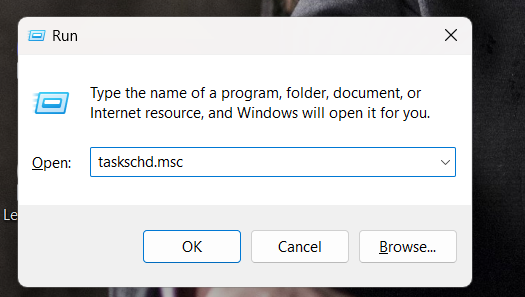
- Press the Windows logo key and R at the same time to open the Run box.
- Type “taskschd.msc” and press Enter.
- Double-click on Task Scheduler Library, then navigate to Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender.
- Double-click Windows Defender Scheduled Scan.
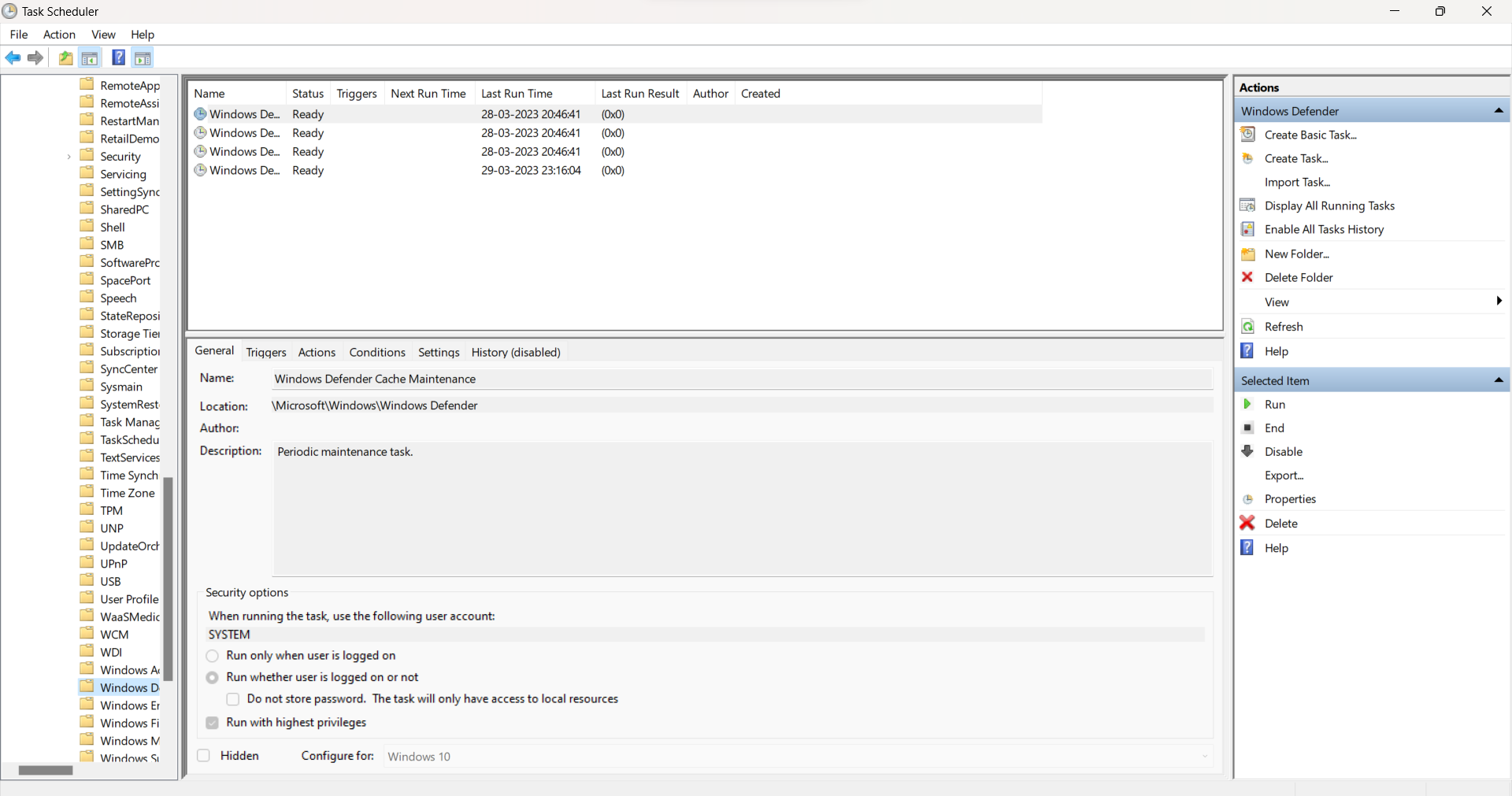
- Uncheck “Run with highest privileges” and uncheck all items in the Conditions section.
- Click OK to save the changes.
If the above steps do not fix the error, don’t worry. There is another method you can try.
3. Check real-time protection settings
Another possible solution to the issue is to disable the real-time protection feature of Windows Defender. Here’s how to do it:
- Press the “Windows logo key + I” simultaneously to open the Settings window.
- Click on Update & Security.
- Under Windows Security, select Virus & threat protection.
- Turn off the Real-time protection feature and wait a minute.
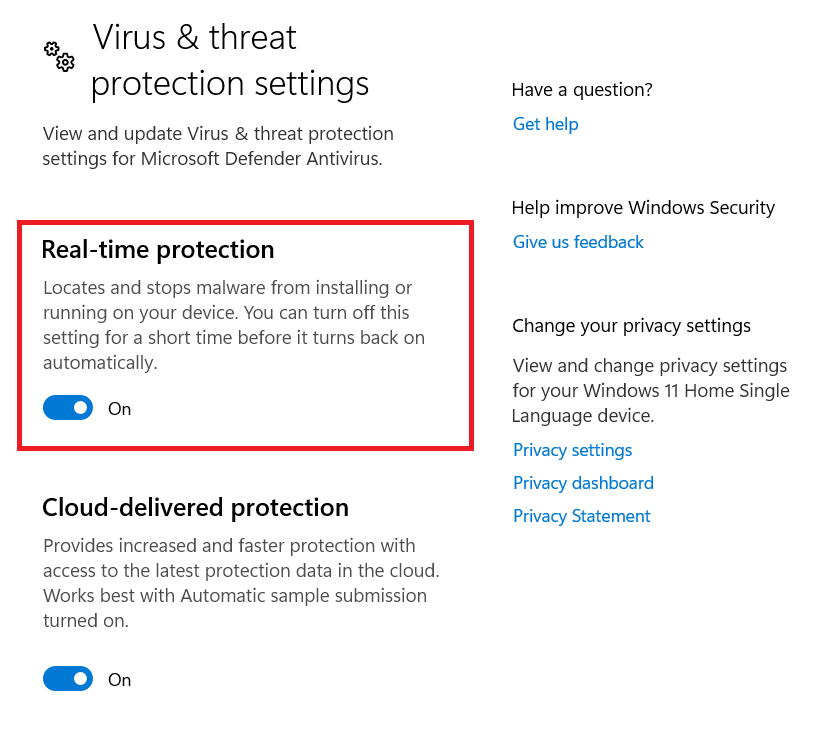
- Turn the Real-time protection feature back on.
This method may resolve the issue, and Windows Defender will continue to protect against threats, but it won’t continuously monitor your PC for potential threats.
Conclusion
The antimalware service executable safeguards your Windows 10 computer against malware threats. If you’ve attempted the methods discussed in this article to reduce its CPU usage and they don’t work, disabling the Windows Security program may be necessary. However, installing another antivirus program is vital to ensure your computer stays protected against potential attacks.







