Overcoming Barriers to Tech Adoption in Global Supply Chains

The global supply chain landscape has witnessed a significant transformation in recent years, largely driven by the adoption of advanced technologies. From Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) to blockchain and robotics, these innovations promise to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve decision-making processes. However, despite the potential benefits, many companies still face substantial barriers when it comes to adopting these technologies. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for organizations aiming to remain competitive in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
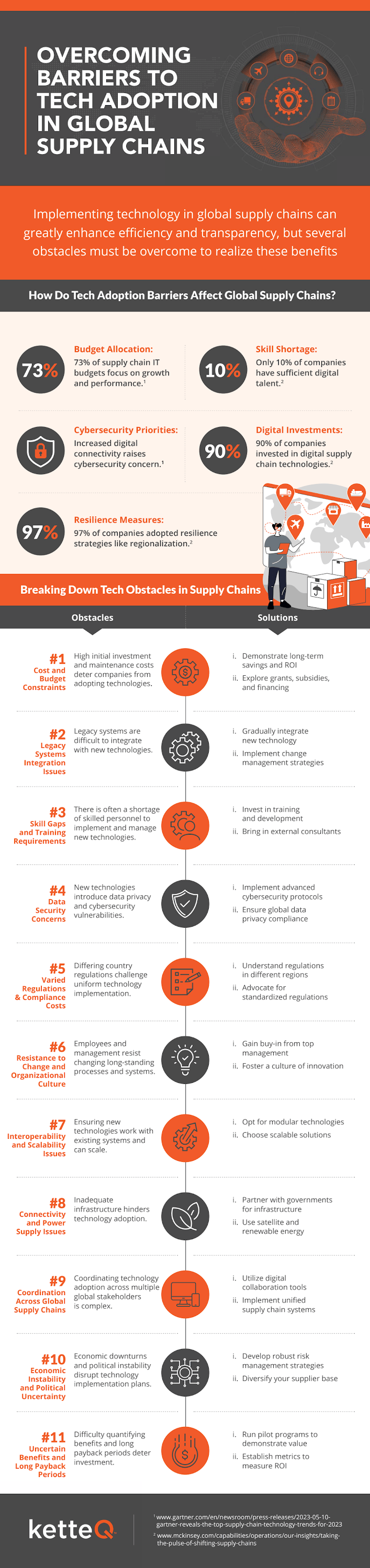
High Initial Investment Costs
One of the primary obstacles to technology adoption in global supply chains is the significant upfront cost. Technologies such as AI, blockchain, and automated systems often require substantial capital investment for both hardware and software, as well as ongoing maintenance and operational expenses. For smaller organizations or companies operating in regions with limited access to capital, these costs can be prohibitively high.
Solution: To address this, companies can explore cloud-based solutions that offer a subscription-based model, reducing the need for hefty upfront investments. Additionally, partnerships and collaborations with tech vendors can provide shared-risk models, making it easier for companies to experiment with and adopt new technologies without a heavy financial burden.
Resistance to Change and Skill Gaps
Another significant barrier is the resistance to change within organizations. Employees, especially those accustomed to traditional systems and processes, may be reluctant to embrace new technologies. This resistance is often fueled by a lack of understanding or fear of job displacement due to automation. Furthermore, there is a widespread shortage of skilled workers capable of managing and operating advanced tech systems, particularly in emerging markets.
Solution: Effective change management is critical. Companies should focus on training and reskilling their workforce to ensure they are prepared for technological shifts. Establishing clear communication about the benefits of technology adoption—such as efficiency gains, job enrichment, and the creation of new roles—can alleviate concerns. Additionally, companies can invest in developing internal talent or collaborate with educational institutions to bridge the skill gap.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Global supply chains involve a complex web of data exchanges between multiple parties, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers. As technologies like IoT and blockchain increase the amount of data generated and shared, concerns about data security and privacy also grow. Organizations must ensure that their systems comply with regional data protection regulations, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), while also safeguarding sensitive business information.
Solution: Organizations should implement robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, secure access controls, and regular security audits. In addition, adopting technologies with built-in security features, such as blockchain’s immutable ledgers, can help mitigate risks. Working with trusted technology vendors who understand the nuances of data security and privacy regulations can also minimize potential vulnerabilities.
Integration with Existing Systems
Supply chains are often built on legacy systems that may not be compatible with modern technologies. The integration of new digital tools with outdated infrastructure can be complex, time-consuming, and costly. Furthermore, the lack of standardization across different parts of the supply chain can further complicate the process.
Solution: A phased approach to technology adoption can help mitigate integration challenges. Companies can begin by adopting modular technologies that are easier to integrate with existing systems. Additionally, focusing on industry standards and working with vendors who prioritize interoperability can reduce the friction associated with system integration.
Lack of Trust and Collaboration Among Stakeholders
In global supply chains, multiple organizations work together, often across borders, to deliver goods and services. Building trust and fostering collaboration among these diverse stakeholders is essential for successful tech adoption. However, different levels of technological readiness, cultural differences, and conflicting priorities can create barriers to cooperation.
Solution: Promoting transparency through technology like blockchain can build trust among supply chain partners by ensuring that all parties have access to real-time, accurate information. Regular communication, joint investments, and shared goals can also encourage collaboration and help overcome mistrust.
Overcoming the barriers to tech adoption in global supply chains is a multifaceted challenge, but it is not insurmountable. By addressing concerns related to cost, resistance to change, data security, integration, and collaboration, organizations can unlock the full potential of technological innovations. As the global economy becomes more interconnected and reliant on digital tools, those that successfully navigate these challenges will gain a significant competitive advantage in the market.
Conclusion
Overcoming the barriers to technology adoption in global supply chains requires a strategic approach that addresses cost, resistance to change, data security, integration, and collaboration. Supply chain planning experts play a crucial role in navigating these challenges by leveraging their expertise to implement innovative solutions, streamline processes, and ensure seamless integration of advanced technologies. Their guidance can help organizations unlock the full potential of digital abilities, driving efficiency and maintaining a competitive edge in the evolving global market.